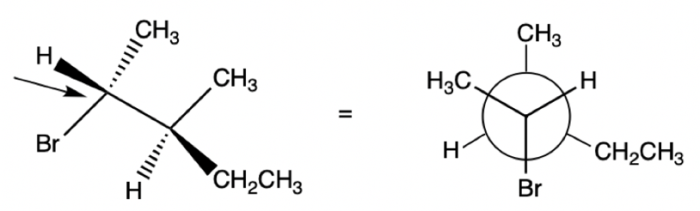Newman projection 1 2 dichloroethane – Newman projections offer a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the three-dimensional structure and conformational behavior of molecules. In this article, we delve into the Newman projection of 1,2-dichloroethane, exploring its unique conformational landscape and the interplay of steric and dipole-dipole interactions that shape its molecular properties.
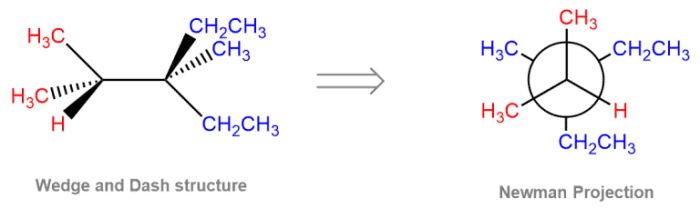
Newman projections provide a simplified representation of a molecule’s three-dimensional structure by projecting the molecule onto a plane. This projection allows us to visualize the relative positions of atoms and functional groups, making it particularly useful for analyzing conformational changes and understanding the molecular basis of physical and chemical properties.
Introduction to Newman Projection of 1,2-Dichloroethane
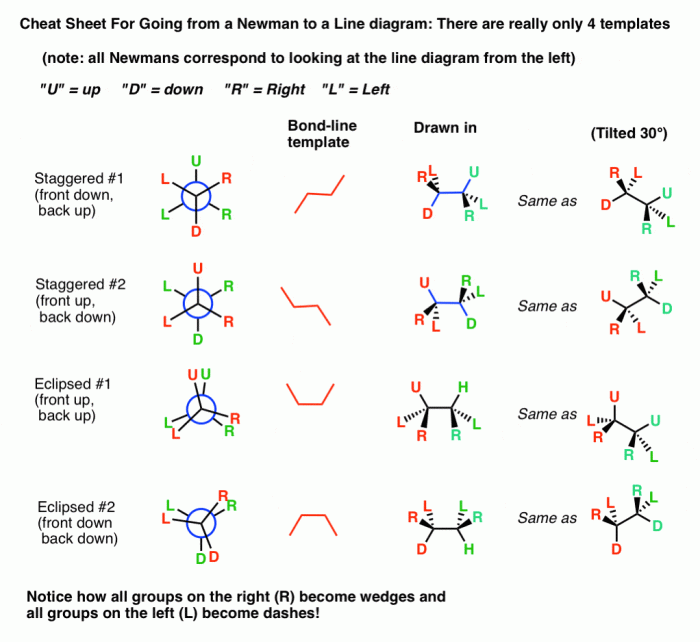
A Newman projection is a two-dimensional representation of a molecule that shows the relative positions of the atoms in space. It is used to visualize the three-dimensional structure of a molecule and to understand its conformational changes.
1,2-Dichloroethane is a molecule with the formula CH 2ClCH 2Cl. It is a colorless liquid that is used as a solvent and as a starting material for the production of other chemicals.
Newman Projection of 1,2-Dichloroethane
The Newman projection of 1,2-dichloroethane is shown below:

In this projection, the carbon atoms are represented by the black dots, and the chlorine atoms are represented by the green dots. The hydrogen atoms are not shown.
The Newman projection shows that the two chlorine atoms are in an anti conformation. This means that they are on opposite sides of the carbon-carbon bond.
Conformational Analysis: Newman Projection 1 2 Dichloroethane
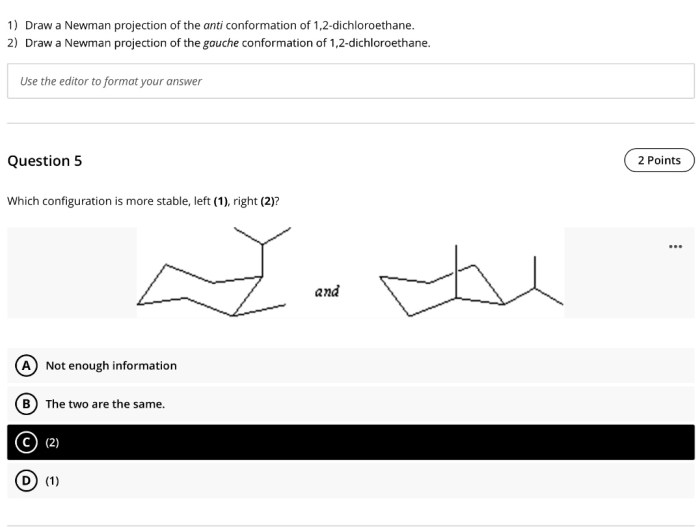
Conformational analysis is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry that describes the different three-dimensional arrangements of atoms within a molecule. These arrangements, known as conformations, are determined by the rotation of bonds and are crucial for understanding the physical and chemical properties of molecules.
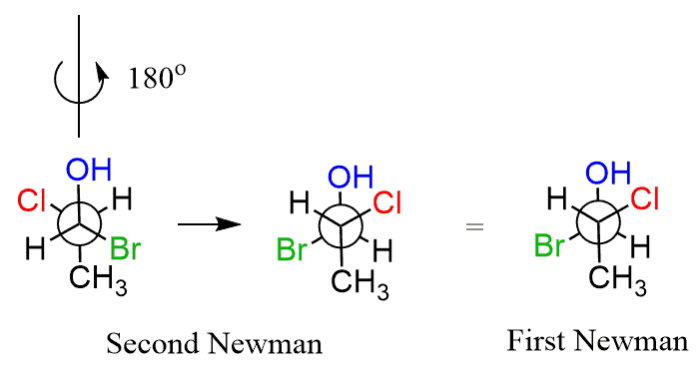
1,2-dichloroethane, a simple organic compound, exists in two distinct conformations: the gauche and anti conformations. The gauche conformation is characterized by the two chlorine atoms being positioned on the same side of the carbon-carbon bond, while in the anti conformation, they are positioned on opposite sides.
Energy Differences Between Conformers
The energy difference between the gauche and anti conformations of 1,2-dichloroethane is a crucial factor in determining the relative stability of each conformation. The gauche conformation is less stable than the anti conformation due to steric hindrance between the chlorine atoms.
This steric hindrance results in a higher energy state for the gauche conformation compared to the anti conformation.
Steric Interactions and Dipole-Dipole Interactions
The stability of different conformations of 1,2-dichloroethane is influenced by both steric interactions and dipole-dipole interactions between the chlorine atoms.
Steric Interactions
In the eclipsed conformation, the chlorine atoms are directly opposite each other, resulting in significant steric hindrance. This repulsive interaction destabilizes the eclipsed conformation.
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
The chlorine atoms in 1,2-dichloroethane are electronegative, creating a permanent dipole moment. In the gauche conformation, the dipole moments of the chlorine atoms are partially aligned, resulting in a dipole-dipole attraction. This attractive interaction stabilizes the gauche conformation.
In contrast, in the anti conformation, the dipole moments of the chlorine atoms are opposed, resulting in a dipole-dipole repulsion. This repulsive interaction destabilizes the anti conformation.
Applications of Newman Projection in 1,2-Dichloroethane
Newman projections provide valuable insights into the physical and chemical properties of 1,2-dichloroethane. By analyzing the relative positions of the atoms in space, Newman projections can predict various properties, including molecular shape, bond lengths, and bond angles.
Predicting Physical and Chemical Properties, Newman projection 1 2 dichloroethane
Newman projections can predict physical properties such as boiling point, melting point, and density. For example, the gauche conformation of 1,2-dichloroethane has a higher boiling point than the anti conformation due to stronger intermolecular dipole-dipole interactions. Newman projections can also predict chemical reactivity, such as the preferred site of electrophilic addition.
In 1,2-dichloroethane, electrophilic addition occurs preferentially at the carbon atom with the fewer chlorine atoms, as predicted by the Newman projection.
Drug Design and Molecular Modeling
Newman projections play a crucial role in drug design and molecular modeling. By understanding the three-dimensional structure of molecules, scientists can design drugs that specifically target and interact with certain proteins or receptors. Newman projections help visualize the steric interactions between molecules and predict their binding affinity.
This information is essential for developing effective and selective drugs.
Environmental Applications
Newman projections have been used to understand the behavior of 1,2-dichloroethane in different environments. For example, Newman projections have been used to study the adsorption of 1,2-dichloroethane onto soil particles and its subsequent degradation. This information is crucial for assessing the environmental fate and transport of 1,2-dichloroethane and developing remediation strategies for contaminated sites.
Common Queries
What is the Newman projection of 1,2-dichloroethane?
The Newman projection of 1,2-dichloroethane is a simplified representation of the molecule’s three-dimensional structure, projected onto a plane. It shows the relative positions of the chlorine atoms and hydrogen atoms along the C-C bond.
How many conformations does 1,2-dichloroethane have?
1,2-dichloroethane has two conformations: the gauche conformation and the anti conformation. In the gauche conformation, the chlorine atoms are on the same side of the C-C bond, while in the anti conformation, they are on opposite sides.
Which conformation of 1,2-dichloroethane is more stable?
The anti conformation of 1,2-dichloroethane is more stable than the gauche conformation due to reduced steric hindrance between the chlorine atoms.